NATO Membership History

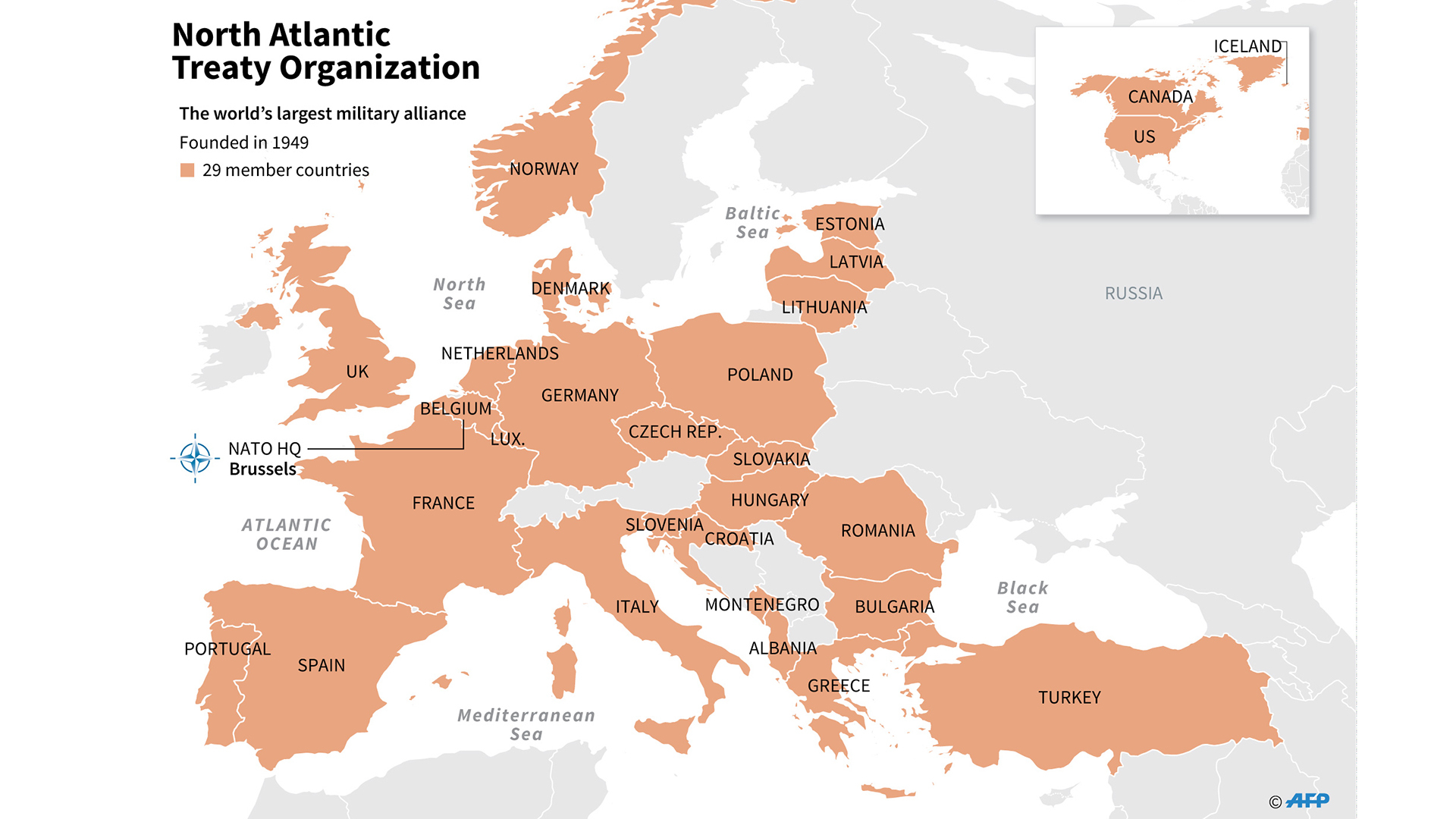
Nato members – The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was established in 1949 by the United States, Canada, and several Western European countries to provide collective security against the Soviet Union and its allies. Since then, NATO has expanded eastward, bringing in new members from Central and Eastern Europe.
The expansion of NATO has been a contentious issue, with Russia viewing it as a threat to its security. However, NATO has argued that its expansion is necessary to protect its members from potential aggression from Russia.
NATO Expansion Timeline
- 1949: NATO is founded by the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Norway, Denmark, Iceland, Italy, and Portugal.
- 1952: Greece and Turkey join NATO.
- 1955: West Germany joins NATO.
- 1982: Spain joins NATO.
- 1999: Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic join NATO.
- 2004: Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia join NATO.
- 2009: Albania and Croatia join NATO.
- 2017: Montenegro joins NATO.
- 2020: North Macedonia joins NATO.
Reasons for NATO Expansion
There are a number of reasons why countries have joined NATO. Some countries, such as Poland and the Czech Republic, joined NATO to protect themselves from potential aggression from Russia. Other countries, such as Spain and Greece, joined NATO to strengthen their ties with the West.
The expansion of NATO has had a significant impact on the geopolitical landscape of Europe and the world. NATO has helped to stabilize Europe and prevent the outbreak of war between its members. NATO has also played a role in promoting democracy and human rights in its member states.
NATO’s Role in Global Security
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is a collective security organization founded in 1949 by the United States, Canada, and several Western European nations to provide mutual defense against the Soviet Union and its allies. Since then, NATO has expanded to include 30 member states and has played a significant role in global security.
NATO’s Mission and Objectives
NATO’s primary mission is to guarantee the security of its member states through political and military means. Its objectives include:
- To maintain peace and stability in the North Atlantic area.
- To deter and defend against aggression from any quarter.
- To promote cooperation among member states in the field of defense and security.
NATO’s Involvement in International Conflicts and Peacekeeping Operations, Nato members
Since its founding, NATO has been involved in numerous international conflicts and peacekeeping operations, including:
- The Korean War (1950-1953)
- The Cold War (1947-1991)
- The Yugoslav Wars (1991-2001)
- The War in Afghanistan (2001-2021)
- The Libyan Civil War (2011)
Challenges and Opportunities Facing NATO in the 21st Century
NATO faces several challenges and opportunities in the 21st century, including:
- The rise of new threats, such as terrorism and cyber warfare.
- The changing geopolitical landscape, including the emergence of new powers such as China and Russia.
- The need to adapt to new technologies and ways of warfare.
Despite these challenges, NATO remains a vital player in global security. Its collective defense system provides a strong deterrent against aggression, and its peacekeeping operations have helped to stabilize conflict zones around the world. As the world continues to change, NATO will need to continue to adapt to meet the new challenges and opportunities that arise.
NATO members gathered in Washington, D.C., for a crucial summit, discussing pressing issues facing the alliance. The summit provided a platform for members to reaffirm their commitment to collective security and to address emerging threats to their shared values. Following the summit, NATO members emerged with a renewed sense of unity and purpose, ready to face the challenges ahead.
NATO members have long relied on the United States for leadership, but that role is now being challenged by Marco Rubio , a Republican senator from Florida who has emerged as a vocal critic of the alliance. Rubio has argued that NATO is no longer relevant to the threats facing the United States and that it is time for the US to reduce its commitment to the alliance.